Wireless communication networks
Crystallization in wireless networks
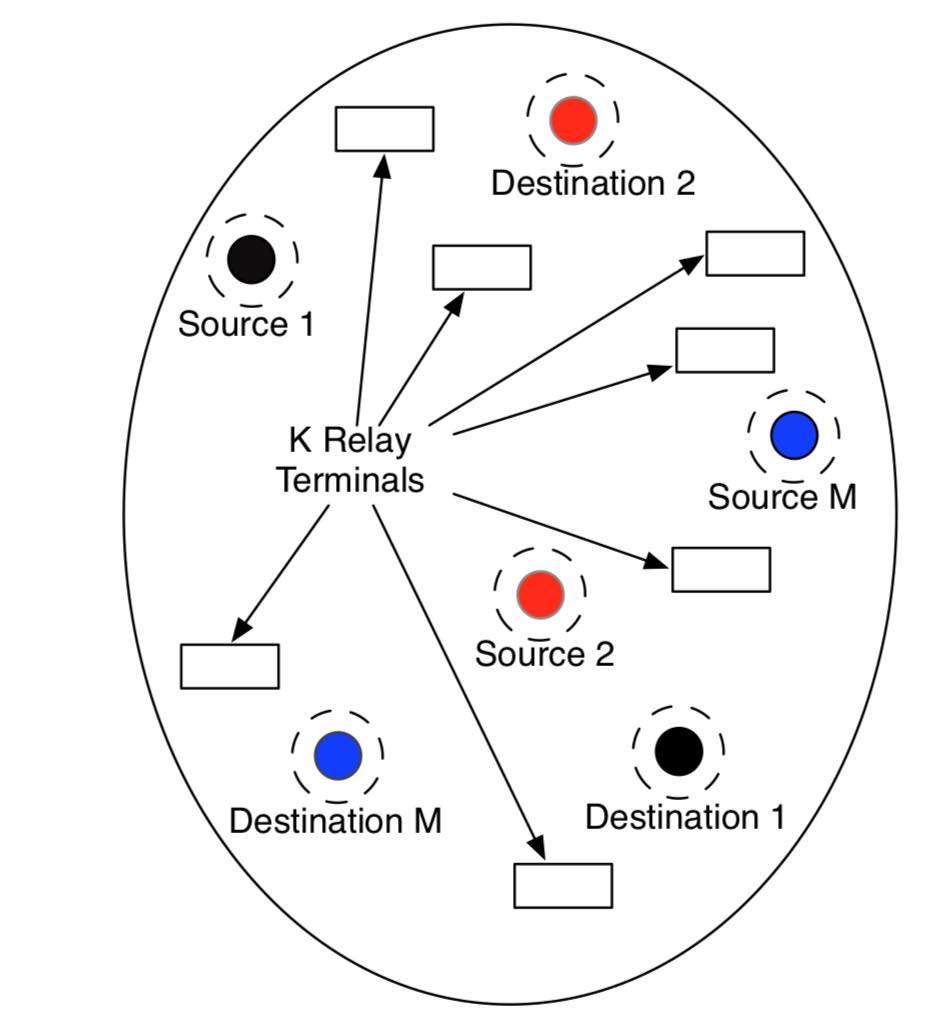 |
In this project, we precisely characterized the performance of a novel relaying protocol for wireless networks that operate with no fixed infrastructure (no base stations). The result of our analysis is the observation that relay devices can completely remove interference and eliminate fading in such wireless system. This principle may be used to develop high-throughput wireless data networks that can be rapidly deployed in an area where base stations do not exist, for example, in an area affected by natural disaster. Mathematically, this work relies on novel concentration inequalities for sums of dependent random variables.
Materials:
Crystallization in large wireless networks V. I. Morgenshtern and H. Bölcskei
IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, Vol. 53, No. 10, pp. 3319–3349, Oct. 2007
Random matrix analysis of large relay networks
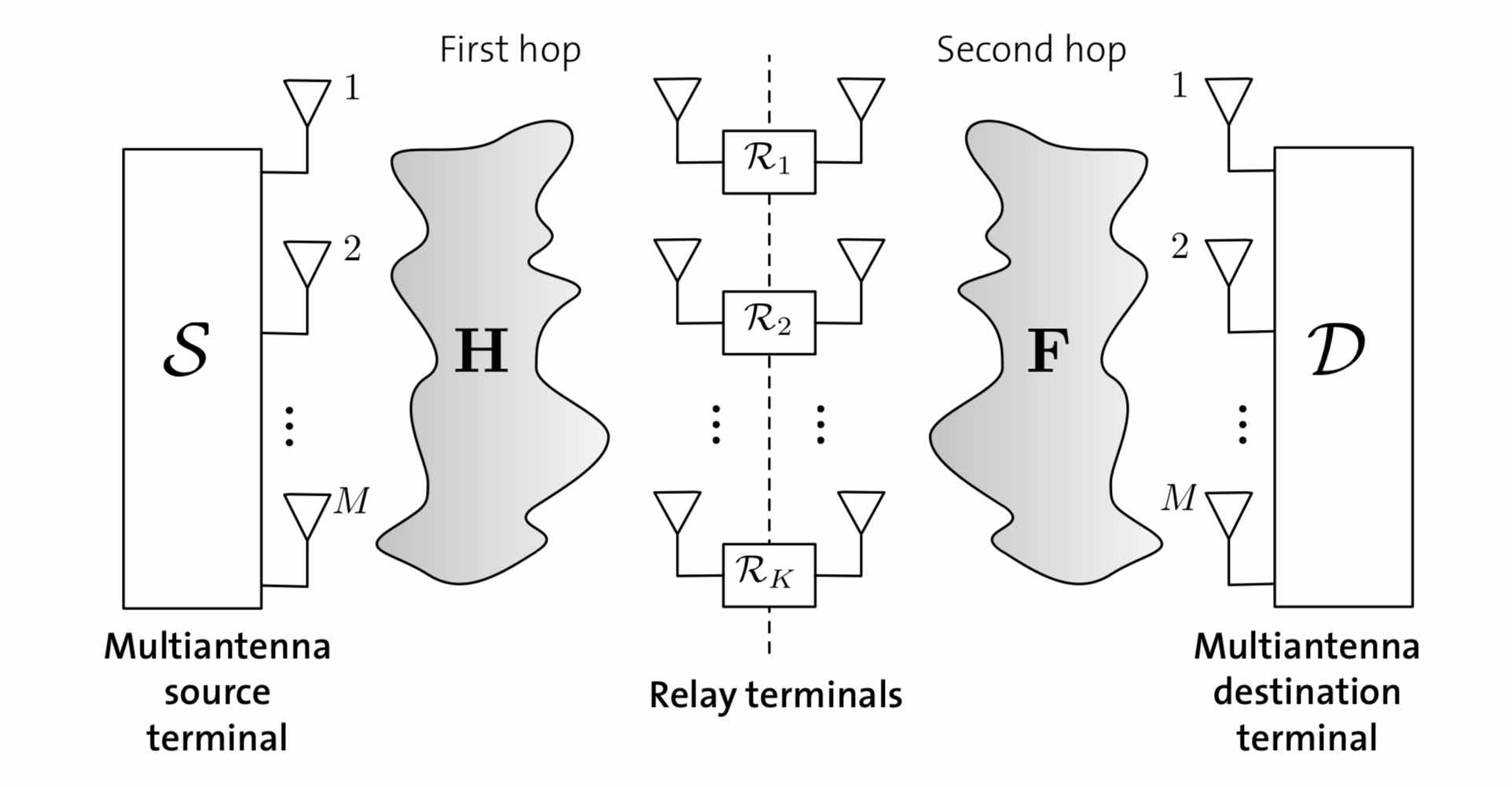 |
In this project, we demonstrated that simple amplify-and-forward relay devices can extend the range of multi-antenna wireless channels without sacrificing performance 5,6. This is useful in the setting where there is no possibility for direct communication between the transmitter and the receiver, as in the case when there is a mountain between them. Mathematically, in this work we derived a law for the limiting eigenvalue distribution of a new class of large random matrices.
Materials:
Random matrix analysis of large relay networks
V. I. Morgenshtern and H. Bölcskei
in Proc. Allerton Conf. Commun., Contr., and Comput., Monticello, IL, pp. 106–112, Sept. 2006, (invited paper)