Super-resolution
Stable super-resolution of positive sources
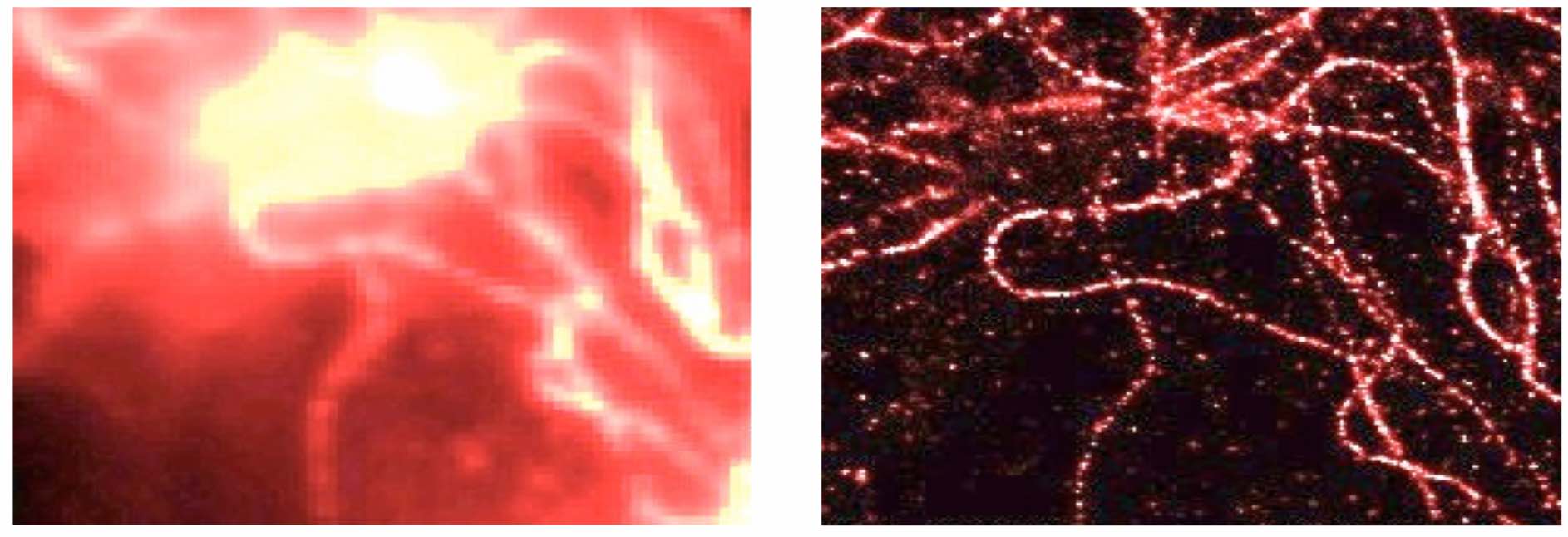 |
In this project, we discovered that an efficient convex optimization algorithm is a near-optimal method for super-resolution of positive sources in the presence of noise. Good algorithms for super-resolution of positive sources are central for future improvements in super-resolved fluorescence microscopy, a method that gives researchers the unique ability to image small structures inside the living cell. The importance of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy is now widely recognized and its inventors were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2014. Mathematically, our work relies on a new interpolation construction in Fourier analysis and on convex duality.
Materials:
Super-resolution of positive sources: the discrete setup
V. I. Morgenshtern and E. J. Candès
SIAM J. on Imaging Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 412–444, Mar. 2016
Super-resolution of positive sources on an arbitrarily fine grid
V. I. Morgenshtern
J. of Fourier Analysis and Appl., 2020, (submitted)
Super-resolution radar
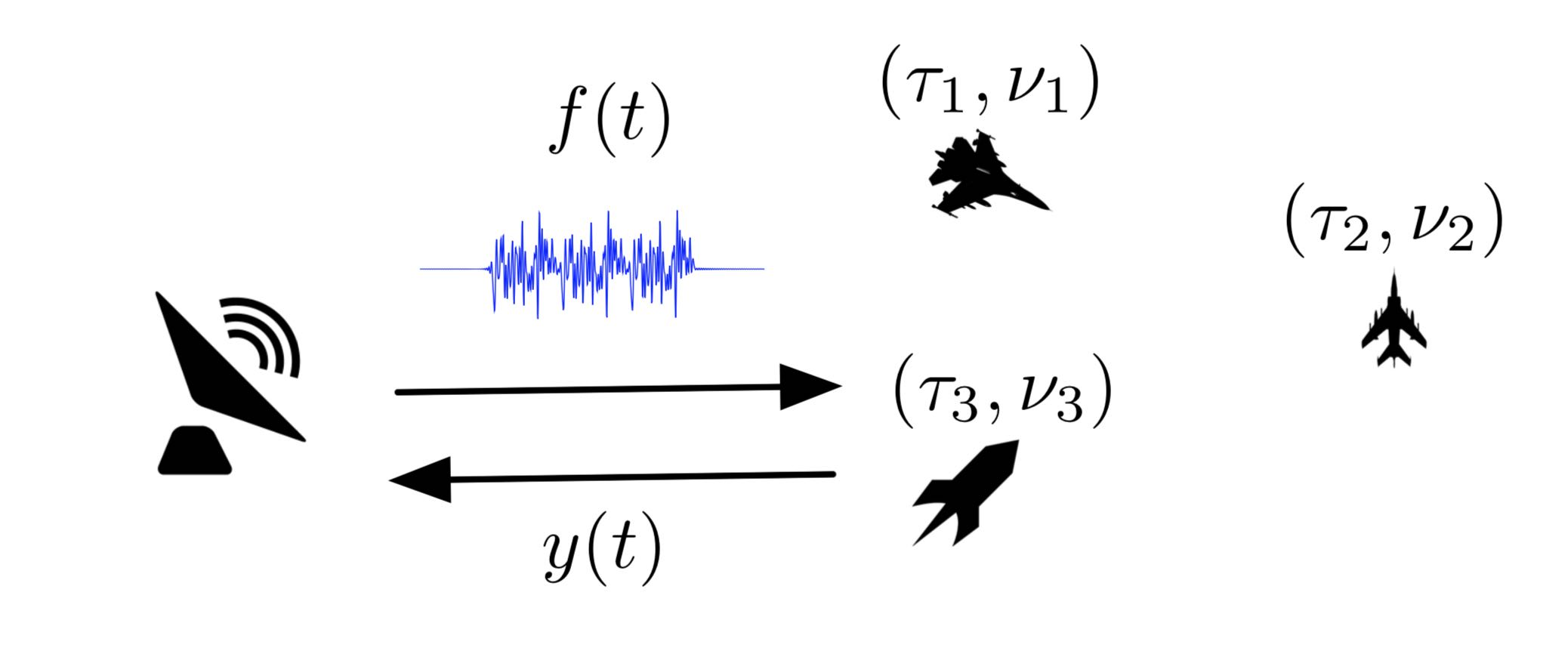 |
The method is based on semidefinite programming and allows to increase the resolution of radar beyond its natural limit. To achieve these gains, it is important to use a random (or pseudorandom) probing signal. Mathematically, this work merges ideas from the theory of super-resolution and the theory of compressed sensing with Gabor dictionary.
Materials:
Super-resolution radar
R. Heckel, V. I. Morgenshtern, and M. Soltanolkotabi
Information and Inference: J. of the IMA, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 22–75